Heng Zeng, Mo Xie, Yong-Liang Huang, Yifang Zhao, Xiao-Jing Xie, Jian-Ping Bai, Meng-Yan Wan, Rajamani Krishna, Weigang Lu,* and Dan Li*
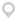
Abstract: Porous materials that can undergo pore-structure adjustment to better accommodate specific molecules are ideal for separation and purification. Here, we report a stable microporous metal-organic framework, JNU-1, featuring onedimensional diamond-shaped channels with a high density of open metal sites arranged on the surface for the cooperative binding of acetylene. Together with its framework flexibility and appropriate pore geometry, JNU-1 exhibits an induced-fit behavior for acetylene. The specific binding sites and continuous framework adaptation upon increased acetylene pressure are validated by molecular modeling and in situ X-ray diffraction study. This unique induced-fit behavior endows JNU-1 with an unprecedented increase in the acetylene binding affinity (adsorption enthalpy: up to 47.6 kJ/mol at ca. 2.0 mmol/g loading).