Xiao-Ping Zhou, Dan Li,* Shao-Liang Zheng, Xuanjun Zhang, and Tao Wu
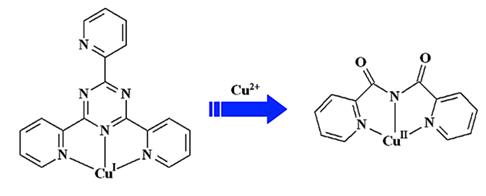
Abstract: The reactions of 2,4,6-tri(2-pyridyl)-1,3,5-triazine (tpt) with copper(I) halides under solvothermal or traditional conditions yielded two polymeric Cu(I) complexes [Cu2I2(tpt)]n (1) and [Cu3I3(tpt)]n (2), one mixed-valence Cu(I)-Cu(II) complex [Cu4Cl2I4(tpt)2] (3), and two Cu(II) complexes [CuBr(bpca)] (4) and [CuI(bpca)] (5) (bpca ) bis(2-pyridylcarbonyl)-amine). Complex 1 is a zigzag chain with tpt in a bis-bipyridine-like coordination mode, whereas complex 2 with tpt chelating three Cu(I) cations is a ladderlike coordination polymer. Complex 3 is mixed-valence, with Cu(I) in a distorted tetrahedral geometry and Cu(II) in a distorted square pyramidal geometry, forming a ladderlike supramolecular chain. Complexes 4 and 5 are the products of in situ hydrolysis of tpt involving the oxidation of Cu(I). The synthesis and characterization of complex 1, 2, and 5 indicated that Cu(I) cannot promote the hydrolysis of tpt. The theoretical study shows that the main effect for hydrolysis of tpt is the electron-withdrawing effect of metal ions.
文章链接:![]() ic060564p.pdf
ic060564p.pdf